Calcium Signaling Controls Pathogenic Th17 Cell-Mediated Inflammation by Regulating Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
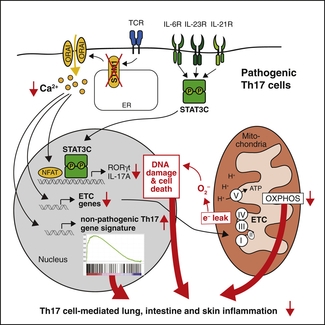
Pathogenic Th17 cells play important roles in many autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Their function depends on T cell receptor (TCR) signaling and cytokines that activate signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). TCR engagement activates stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and calcium (Ca2+) influx through Ca2+-release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channels. Here, we show that abolishing STIM1 and Ca2+ influx in T cells expressing a hyperactive form of STAT3 (STAT3C) attenuates pathogenic Th17 cell function and inflammation associated with STAT3C expression. Deletion of STIM1 in pathogenic Th17 cells reduces the expression of genes required for mitochondrial function and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) but enhances reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. STIM1 deletion or inhibition of OXPHOS is associated with a non-pathogenic Th17 gene expression signature and impaired pathogenic Th17 cell function. Our findings establish Ca2+ influx as a critical regulator of mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in pathogenic Th17 cell-mediated multiorgan inflammation.
Be the first to leave a comment!